You can view live values by using Tonviewer.
Prerequisites
This material should be read alongside the parameter list. You can view the parameter values in the current configuration, and the method of writing them into cells is outlined in theblock.tlb file in TL-B format.
Configuration values are TL-B typed cells serialized into Bags of Cells (BoC).
Param 0: config address
This parameter is the address of a special smart contract that stores the blockchain’s configuration. The configuration is stored in the contract to simplify its loading and modification during validator voting.In the configuration parameter, only the hash portion of the address is recorded, as the contract always resides in the masterchain (workchain -1). Therefore, the full address of the contract will be written as
-1:<value of the configuration parameter>.Param 1: elector address
This parameter is the address of the elector smart contract, responsible for appointing validators, distributing rewards, and voting on changes to blockchain parameters. Parameter #1 on mainnetParam 2: TON minting address
This parameter represents the address of the system, on behalf of which new Toncoin are minted and sent as rewards for validating the blockchain.If parameter 2 is missing, parameter 0 is used instead (newly minted Toncoin come from the configuration smart contract).
Param 3: fee collector address
This parameter is the address of the transaction fee collector.If this parameter is missing (for the time being), transaction fees are directed to the elector smart contract (parameter 1).
Param 4: root DNS address
This parameter is the address of the root DNS contract of the TON network.For details, see the original specification.This contract is not responsible for selling .ton domains.
Param 6: extra currency fee
This parameter is responsible for minting fees for new currencies. Parameter #6 on mainnetParam 7: extra currency volume
This parameter stores the volume of each extra currency in circulation. The data is organized as a dictionary (also referred to as a hashmap). The structure uses the formatcurrency_id -> amount, where the amount is represented as a VarUInteger 32, which is an integer ranging from 0 to 2^248-1.
Parameter #7 on mainnet
Param 8: network version
This parameter indicates the network version and additional capabilities supported by the validators.Validators are nodes in the TON Blockchain network that are responsible for creating new blocks and verifying transactions.
-
version: This field specifies the version. -
capabilities: This field is a set of flags that are used to indicate the presence or absence of certain features or capabilities.
Param 9: mandatory params
This parameter contains a list (binary tree) of mandatory parameters. It ensures that certain configuration parameters are always present and cannot be removed by a proposal to change the configuration until parameter 9 changes. Parameter #9 on mainnetParam 10: critical params
This parameter represents a list (binary tree) of critical TON parameters whose change significantly affects the network, so more voting rounds are held. Parameter #10 on mainnetParam 11: config params
This parameter indicates under what conditions proposals to change the TON configuration are accepted.-
min_tot_rounds: The minimum number of rounds before a proposal can be applied. Currently, this parameter is not used: onlymax_tot_round(when the proposal will be rejected) andmin_wins(when the proposal will be accepted) matter. -
max_tot_rounds: The maximum number of rounds, upon reaching which the proposal will automatically be rejected -
min_wins: The required number of wins (3/4 of validators by the sum of the pledges must vote in favor) -
max_losses: The maximum number of losses, upon reaching which the proposal will automatically be rejected -
min_store_secandmax_store_secdetermine the possible time interval during which the proposal will be stored -
bit_priceandcell_priceindicate the price of storing one bit or one cell of the proposal
Param 12: Workchain config
This parameter represents the configuration of a workchain in the TON Blockchain. workchains are designed as independent blockchains that can operate in parallel, allowing TON to scale and process a large number of transactions and smart contracts.Workchain configuration parameters
-
enabled_since: A UNIX timestamp of the moment this workchain was enabled. -
actual_min_split: The minimum depth of the split (sharding) of this workchain, supported by validators. -
min_split: The minimum depth of the split of this workchain, set by the configuration. -
max_split: The maximum depth of the split of this workchain. -
basic: A boolean flag (1 for true, 0 for false) indicating whether this workchain is basic (handles TON coins, smart contracts based on the TON Virtual Machine). -
active: A boolean flag indicating whether this workchain is active at the moment. -
accept_msgs: A boolean flag indicating whether this workchain is accepting messages at the moment. -
flags: Additional flags for the workchain (reserved, currently always 0). -
zerostate_root_hashandzerostate_file_hash: Hashes of the first block of the workchain. -
version: Version of the workchain. -
format: The format of the workchain, which includesvm_versionandvm_mode- the virtual machine used there.
Param 13: complaint cost
This parameter defines the cost of filing complaints about the incorrect operation of validators in the elector smart contract. Parameter #13 on mainnetParam 14: block reward
This parameter indicates the reward for creating a block in the TON Blockchain. Values are in nanotons (also referred to as nanograms); therefore, the reward for block creation in the masterchain is 1.7 Toncoin, while in the basechain, it is 1.0 Toncoin. In the event of a workchain split, the block reward is also divided: if there are two shardchains within the workchain, then the reward for each shard block will be 0.5 Toncoin. Parameter #14 on mainnetParam 15: elections timing
This parameter contains the duration of different stages of elections and validators’ work in the TON Blockchain. For each validation period, there is anelection_id equal to the UNIX-format time at the start of the validation.
You can get the current election_id (if elections are ongoing) or the past one by invoking the elector smart contract’s respective get-methods active_election_id and past_election_ids.
Election and validation timing parameters
-
validators_elected_for: The number of seconds the elected validators perform their role (one round). -
elections_start_before: The seconds before the end of the current round, when the election process for the next period will start. -
elections_end_before: The seconds before the end of the current round, the validators for the next round will be chosen. -
stake_held_for: The period for which a validator’s stake is held (for handling complaints) after the round expires.
Each value in the arguments is determined by the
uint32 data type.Examples
In the TON Blockchain, validation periods are typically divided into even and odd rounds that alternate. Voting for the next round occurs during the previous one, so a validator must allocate their funds into two separate pools to participate in both rounds.Mainnet
Current values: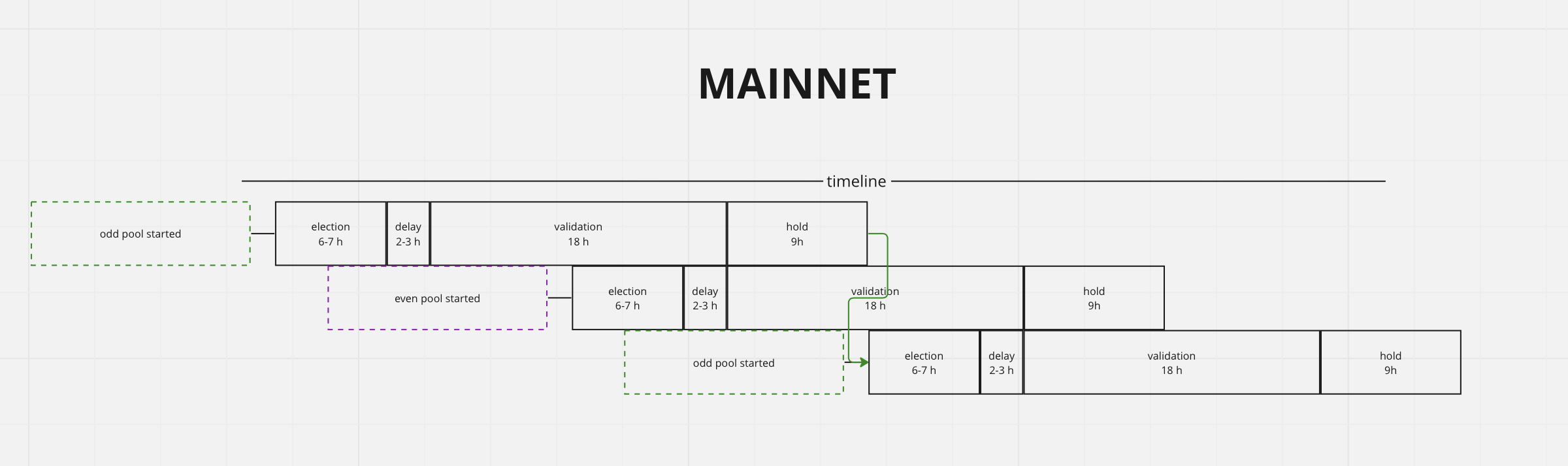

How to calculate periods?
Letelection_id = validation_start = 1600032768. Then:
1600131072 - 1600000000 = 131072 seconds = 36.40888... hours
Testnet
Current values: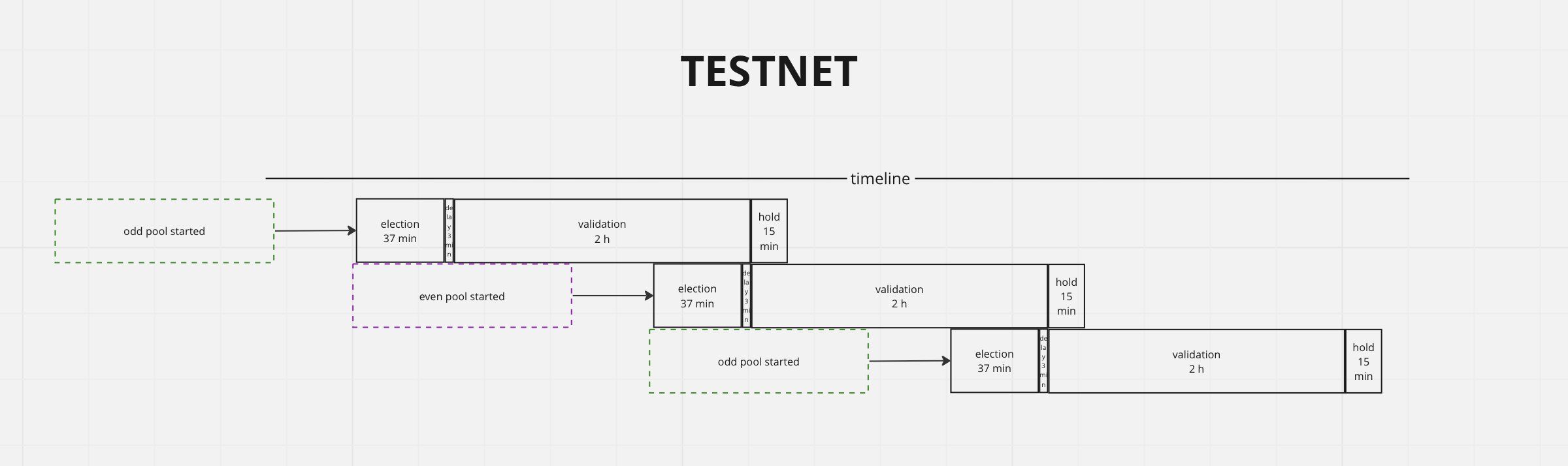

How to calculate periods?
Letelection_id = validation_start = 160002400. Then:
160010500 - 160000000 = 10500 seconds = 175 minutes = 2.91666... hours
Parameter #15 on mainnet
Param 16: validators limits
This parameter represents the limits on the number of validators in the TON Blockchain. It is directly used by the elector smart contract.Configuration parameters for the number of validators for elections
-
max_validators: This parameter represents the maximum number of validators that can participate in the network operation at any given time. -
max_main_validators: This parameter represents the maximum number of masterchain validators. -
min_validators: This parameter represents the minimum number of validators that must support the network operation.
Notes
- The maximum number of validators is greater than or equal to the maximum number of masterchain validators.
- The maximum number of masterchain validators must be greater than or equal to the minimum number of validators.
- The minimum number of validators must be no less than 1.
Param 17: stake limits
This parameter represents the stake parameters configuration in the TON Blockchain. In many blockchain systems, especially those using the Proof-of-Stake or Delegated Proof-of-Stake consensus algorithm, cryptocurrency owners native to the network can “stake” their tokens to become validators and earn rewards.Configuration parameters
-
min_stake: This parameter represents the minimum amount of Toncoin that an interested party needs to stake to participate in the validation process. -
max_stake: This parameter represents the maximum amount of Toncoin that an interested party can stake. -
min_total_stake: This parameter represents the minimum total amount of Toncoin that the chosen set of validators must hold. -
max_stake_factor: This parameter is a multiplier indicating how many times the maximum effective stake (pledge) can exceed the minimum stake sent by any other validator.
Each value in the arguments is determined by the
uint32 data type.Param 18: storage prices
This parameter represents the configuration for determining the prices for data storage on the TON Blockchain. This serves as a measure to prevent spam and encourages network maintenance.Dictionary of storage fee parameters
-
utime_since: This parameter provides the initial Unix timestamp from which the specified prices apply. -
bit_price_psandcell_price_ps: These parameters represent the storage prices for one bit or one cell of information in the main workchains of the TON Blockchain for 65536 seconds. -
mc_bit_price_psandmc_cell_price_ps: These parameters represent the storage prices per bit and per cell in the TON masterchain for 65536 seconds.
utime_since accepts values in the uint32 data type.The rest accept values in the uint64 data type.Param 20 and 21: gas prices
These parameters define the cost of computations in the TON network. The complexity of any computation is estimated in gas units. Note: Param 20 defines gas settings for the masterchain; Param 21 defines gas settings for other workchains.-
flat_gas_limitandflat_gas_price: A certain starting amount of gas is provided at a price offlat_gas_price(to offset the costs of launching the TON Virtual Machine). -
gas_price: This parameter reflects the price of gas in the network, in nanotons per 65536 gas units. -
gas_limit: This parameter represents the maximum amount of gas that can be consumed per transaction. -
special_gas_limit: This parameter represents the limit on the amount of gas that can be consumed per transaction of a special (system) contract. -
gas_credit: This parameter represents a credit in gas units provided to transactions to process an external message. -
block_gas_limit: This parameter represents the maximum amount of gas that can be consumed within a single block. -
freeze_due_limitanddelete_due_limit: Limits of accumulated storage fees (in nanotons) at which a contract is frozen and deleted, respectively.
You can find more about
gas_credit and other parameters in the section of external messages here.Param 22 and 23: block limits
These parameters set limits on the block, upon reaching which the block is finalized and the callback of the remaining messages (if any) is carried over to the next block.Configuration parameters
-
bytes: This section sets the limits on the block size in bytes. -
underload: Underload is a state when the shard realizes that there is no load and is inclined to merge if a neighboring shard is willing. -
soft_limit: Soft limit - when this limit is reached, internal messages stop being processed. -
hard_limit: Hard limit - this is the absolute maximum size. -
gas: This section sets the limits on the amount of gas that a block can consume. Gas, in the context of blockchain, is an indicator of computational work. The limits on underload, soft and hard limits work the same as for size in bytes. -
lt_delta: This section sets the limits on the difference in logical time between the first and last transaction. Logical time is a concept used in the TON Blockchain for ordering events. The limits on underload, soft and hard limits work the same as for size in bytes and gas.
If a shard has insufficient load and there is an intention to merge with a neighboring shard, the
soft_limit indicates a threshold. When this threshold is exceeded, internal messages will stop being processed, while external messages will still be handled. External messages will continue to be processed until the total reaches a limit that is equal to half the sum of the soft_limit and hard_limit, or (soft_limit + hard_limit) / 2.Param 24 and 25: message price
Parameter 24 represents the configuration for the cost of sending messages in the masterchain of the TON Blockchain. Parameter 25 represents the configuration for the cost of sending messages in all other cases.Configuration parameters defining the costs of forwarding
-
lump_price: This parameter means the base price for forwarding a message, regardless of its size or complexity. -
bit_price: This parameter represents the cost per bit of message forwarding. -
cell_price: This parameter reflects the cost of forwarding a message per cell. A cell is the basic unit of data storage on the TON Blockchain. -
ihr_price_factor: This is a factor used to calculate the cost of immediate hypercube routing (IHR).
IHR is a method of message delivery in the TON Blockchain network, where messages are sent directly to the recipient’s shardchain.
-
first_frac: This parameter defines the fraction of the remaining amount that will be used for the first transition along the message route. -
next_frac: This parameter defines the fraction of the remaining amount that will be used for subsequent transitions along the message route.
Param 28: catchain config
This parameter provides the configuration for theCatchain protocol in the TON Blockchain. Catchain is the lowest-level consensus protocol used in the TON to achieve agreement among validators.
Configuration parameters
-
flags: A general field that can be used to set various binary parameters. In this case, it equals 0, which means that no specific flags are set. -
shuffle_mc_validators: A Boolean value indicating whether to shuffle the masterchain validators or not. If this parameter is set to 1, the validators will be shuffled; otherwise, they will not. -
mc_catchain_lifetime: The lifetime of masterchain’sCatchaingroups in seconds. -
shard_catchain_lifetime: The lifetime of shardchain’sCatchaingroups in seconds. -
shard_validators_lifetime: The lifetime of a shardchain’s validators group in seconds. -
shard_validators_num: The number of validators in each shardchain validation group.
Param 29: consensus config
This parameter provides the configuration for the consensus protocol aboveCatchain (Param 28) in the TON Blockchain. The consensus protocol is a crucial component of a blockchain network, and it ensures that all nodes agree on the state of the distributed ledger.
Configuration parameters
-
flags: A general field that can be used to set various binary parameters. -
new_catchain_ids: A Boolean value indicating whether to generate newCatchainidentifiers. -
round_candidates: The number of candidates to be considered in each round of the consensus protocol. -
next_candidate_delay_ms: The delay in milliseconds before the right to generate a block candidate passes to the next validator. -
consensus_timeout_ms: The timeout for block consensus in milliseconds. -
fast_attempts: The number of “fast” attempts to reach consensus. -
attempt_duration: The duration of each attempt at agreement, in seconds. -
catchain_max_deps: The maximum number of dependencies of a Catchain block. -
max_block_bytes: The maximum size of a block in bytes. -
max_collated_bytes: The maximum size of serialized block correctness proofs in bytes. -
proto_version: The protocol version. -
catchain_max_blocks_coeff: The coefficient limiting the rate of block generation inCatchain, description.
Param 31: fee-exempt contracts
This parameter represents the configuration of smart contract addresses from which no fees are charged for either gas or storage, and where tick-tock transactions can be created. The list usually includes governance contracts. The parameter is presented as a binary tree structure — a tree (HashMap 256), where the keys are a 256-bit representation of the address. Only addresses in the masterchain can be present in this list. Parameter #31 on mainnetParam 32, 34, and 36: validator lists
Lists of validators from the previous (32), current (34), and next (36) rounds. Parameter 36 is set from the end of the elections until the start of the round.Configuration parameters
-
cur_validators: This is the current list of validators. Validators are typically responsible for verifying transactions in a blockchain network. -
utime_sinceandutime_until: These parameters provide the time period during which these validators are active. -
totalandmain: These parameters provide the total number of validators and the number of validators validating the masterchain in the network. -
total_weight: This adds up the weights of the validators. -
list: A list of validators in the tree formatid->validator-data:validator_addr,public_key,weight,adnl_addr: These parameters provide details about each validator - their 256-bit addresses in the masterchain, public key, weight, ADNL address (the address used at the network level of the TON).
Param 40: misbehavior punishment
This parameter defines the structure of the configuration for punishment for improper behavior (non-validation). In the absence of the parameter, the default fine size is 101 Toncoin.Configuration parameters
MisbehaviourPunishmentConfig: This data structure defines how improper behavior in the system is punished.
It contains several fields:
-
default_flat_fine: This part of the fine does not depend on the stake size. -
default_proportional_fine: This part of the fine is proportional to the validator’s stake size. -
severity_flat_mult: This is the multiplier applied to thedefault_flat_finevalue for significant violations by the validator. -
severity_proportional_mult: This is the multiplier applied to thedefault_proportional_finevalue for significant violations by the validator. -
unpunishable_interval: This parameter represents the period during which offenders are not punished to eliminate temporary network problems or other anomalies. -
long_interval,long_flat_mult,long_proportional_mult: These parameters define a “long” period of time and multipliers for flat and proportional fines for improper behavior. -
medium_interval,medium_flat_mult,medium_proportional_mult: Similarly, they define a “medium” period of time and multipliers for flat and proportional fines for improper behavior.
Param 43: account and message limits
This parameter relates to the size limits and other features of accounts and messages.Configuration parameters
-
max_msg_bits: Maximum message size in bits. -
max_msg_cells: Maximum number of cells (a form of storage unit) a message can occupy. -
max_library_cells: Maximum number of cells that can be used for library cells. -
max_vm_data_depth: Maximum cell depth in messages and account state. -
max_ext_msg_size: Maximum external message size in bits. -
max_ext_msg_depth: Maximum external message depth. This could refer to the depth of the data structure within the message. -
max_acc_state_cells: Maximum number of cells that an account state can occupy. -
max_acc_state_bits: Maximum account state size in bits.
-
max_size= 65535 -
max_depth= 512 -
max_msg_bits= 1 << 21 -
max_msg_cells= 1 << 13 -
max_library_cells= 1000 -
max_vm_data_depth= 512 -
max_acc_state_cells= 1 << 16 -
max_acc_state_bits= (1 << 16) * 1023
You can view more details about the standard parameters here in the source code.
Param 44: suspended addresses
This parameter defines the list of suspended addresses, which cannot be initialized untilsuspended_until. It only applies to yet uninitiated accounts. This is a measure for stabilizing the tokenomics (limiting early miners). If not set, there are no limitations. Each address is represented as an end node in this tree, and the tree-like structure allows efficient checking of whether an address is in the list.
The stabilization of the tokenomics is further described in the official report of the
@tonblockchain Telegram channel.Param 45: precompiled contracts
The list of precompiled contracts is stored in the masterchain config:Param 71 - 73: outbound bridges
This parameter pertains to bridges for wrapping Toncoin in other networks:- ETH-TON (71)
- BNB-TON (72)
- Polygon-TON (73)
Configuration parameters
-
bridge_address: This is the bridge contract address that accepts TON to issue wrapped Toncoin in other networks. -
oracle_multisig_address: This is the bridge management wallet address. A multisig wallet is a type of digital wallet that requires signatures from multiple parties to authorize a transaction. It is often used to increase security. The oracles act as the parties. -
oracles: List of oracles in the form of a treeid->address -
external_chain_address: This is the bridge contract address in the corresponding external blockchain.
Param 79, 81, and 82: inbound bridges
This parameter relates to bridges for wrapping tokens from other networks into tokens on the TON network:- ETH-TON (79)
- BNB-TON (81)
- Polygon-TON (82)
Configuration parameters
-
bridge_addressandoracles_address: These are the blockchain addresses of the bridge and the bridge management contract (oracles multisig), respectively. -
oracles: List of oracles in the form of a treeid->address -
state_flags: State flag. This parameter is responsible for enabling/disabling separate bridge functions. -
prices: This parameter contains a list or dictionary of prices for different operations or fees associated with the bridge, such asbridge_burn_fee,bridge_mint_fee,wallet_min_tons_for_storage,wallet_gas_consumption,minter_min_tons_for_storage,discover_gas_consumption. -
external_chain_address: The bridge contract address in another blockchain.
Negative parameters
Validators enforce TL-B validity only for configuration parameters with non-negative indices. Values with negative indices are not validated against a specific
ConfigParam i type. See the explanation in Configuration parameters section.Next steps
After thoroughly reviewing this article, it is highly recommended that you dedicate time to a more in-depth study of the following documents:- The original descriptions are present, but they may be limited, in the documents:
- Source code: