- A flexible multi-blockchain platform with Turing-complete smart contracts (TON Blockchain)
- A peer-to-peer network used by Blockchain Nodes (TON Network)
- A distributed file storage technology (TON Storage)
- A network proxy/anonymizer layer (TON Proxy)
- A Kademlia-like distributed hash table (TON DHT)
- A service for assigning human-readable names to accounts, smart contracts, services, and network nodes (TON DNS)
- A platform for micro-payments (TON Payments)
TON Network
TON Network is a peer-to-peer network used for accessing the TON Blockchain, sending transactions, and receiving updates. Also, it can support arbitrary distributed services, blockchain-related or not. The cornerstone in TON networking is the ADNL protocol, built on top of the TCP/UDP stack. The TON Distributed Hash Table (DHT) plays a crucial role in the networking component of the TON Project, as it is used to locate other nodes in the network. You can think of it as a big, persistent key-value data storage. The keys of the TON DHT are simply 256-bit integers. In most cases, they are computed as sha256 hashes of a TL-serialized objects. The values assigned to these 256-bit keys are essentially arbitrary byte strings of limited length.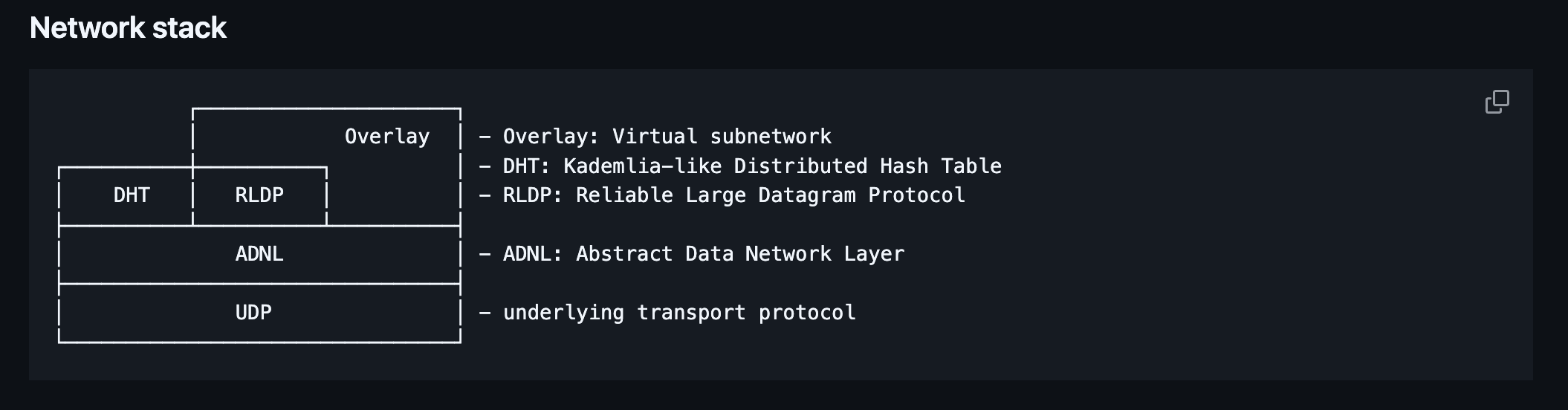

TON Storage
TON Storage allows users to share and store files using The Open Network. Since storing files on-chain isn’t practical, TON Storage only stores Merkle proofs for file content on-chain. It uses TON DHT to find the nodes that have a copy of a required file (e.g., a snapshot of the state of a shardchain, or an old block). Then, one might essentially create a torrent for this file and use TON DHT as a “distributed torrent tracker” for this torrent.TON Proxy
TON Proxy provides a protocol where nodes wishing to offer their services (with or without compensation) as tunnels for ADNL network traffic can register. Those needing them can then choose one of these nodes based on the price, latency, and bandwidth offered. Since ADNL traffic is encrypted, Proxy can’t access tunneled data, meaning that this protocol is secure. Running TON Proxy allows you to visit TON Sites (HTTP over ADNL). This can be combined with TON DNS and other TON Services, forming together what is called “Open Network”.TON DNS
TON DNS is a service that translates human-readable domain names liketest.ton or mysite.temp.ton into TON smart contract addresses, ADNL addresses used by services on the TON Network such as TON Sites, and more. The standard is implemented using smart contracts and config parameters.
TON Domain names are well-established in the ecosystem - various wallet applications and explorers recognize them.
TON Domains can be assigned to any ADNL address, meaning that it is possible to assign names to TON Storage files (bags).