| Ecosystem | Tools and libraries for developing on TON, and how to use them. |
| Payment processing | Guides on monitoring and handling blockchain transactions for business applications, such as exchanges. |
| Standard contracts | Working with most popular standardized contracts. |
| Contract development | Guides on developing smart-contracts. |
| Languages | Reference documentation for TON-specific languages. |
| TON Virtual Machine | Description of the low-level language that runs smart-contracts, and details of the runtime. |
| Blockchain foundations | Comprehensive description of the blockchain. Includes web version of whitepapers. |
| Contribute | Documentation on writing this documentation. |
This is a condensed description of TON. The rest of the documentation may assume that all of this is already known to the reader.
To start building on TON, begin with Your first smart contract.
TON overview
TON is a blockchain. It provides a distributed platform for storing data and code, as well as running computations, all the ingredients to host applications. Roughly speaking, it works as if it were a single server executing all the code. The hosted applications are called smart-contracts. The platform runs on a set of servers, called nodes. Most important type of nodes, validators, are owned by individuals or organizations with a large stake in TON and great interest in keeping the platform safe, fair, and operational. Validators have to reach consensus on the state of the blockchain. Typically, the process takes 5 seconds to reach transaction finality, a time to mint a new block.Network communication
The nodes that run the blockchain interact via the ADNL protocol. User-facing applications usually use servers that proxy JSON HTTP requests into the ADNL network. The official version of such a proxy server is provided by the liteserver software. There are public instances of liteserver, so developers are not required to host one on their own servers.Toncoin and fees
Toncoin is TON’s primary cryptocurrency. It is used to pay for the execution of smart contracts, the storage of their data, and network traffic. Such payments are called fees.Mainnet and testnet
There are two instances of TON blockchain: mainnet and testnet. Mainnet is the “real” network. It’s where actual payments in Toncoin are made. Applications use the mainnet by default. The other network is testnet, and it is used by TON developers to check that their applications work correctly before deploying them to mainnet. It uses “test coins” that barely have any value. Usually, when the TON blockchain gets an update, it is first deployed to testnet, and then to mainnet after a brief period of testing, so sometimes they may run different software. Also, their configuration, availability, and throughput might be different.Workchains and shards
Each network is split into workchains that can freely interact with each other, but their implementations may differ significantly. At the moment, there are two workchains: basechain (workchain_id = 0) for regular use, and a very similar masterchain (workchain_id = -1) for TON’s internal bookkeeping. The masterchain follows mostly the same rules, except that using it is more expensive to limit the amount of traffic that interferes with TON’s internals.
To be freely scalable, each workchain is split into shards. The number of shards is determined dynamically based on the current network load. Internally, every shard is implemented as a separate blockchain. Except for increased latency, the effect on the user-facing code is minimal.
Accounts
It’s easiest to visualize the blockchain as a set of accounts. Each account has an address and a status.Account statuses
Over its lifetime, an account changes its status among four values:nonexist: There wasn’t a single operation with the account, or it was removed. It has neither a balance, nor code.uninit: If some Toncoin is transferred to an account, it now exists, but there is still no smart contract code on it. It now has a balance.active: After a deploy message (see below) with code and initial data is sent to an account, it becomes active and can process other messages. It now has a balance, code, and internal state.frozen: If an account is overdue on its storage fees, it will be frozen until the fees are paid. If the overdue amount reaches a maximum limit specified by the blockchain, the account goes completely bankrupt, is removed, and ceases to exist.
Smart contracts
The code on an active account is a smart contract. The term contract is often used for an account that holds the code.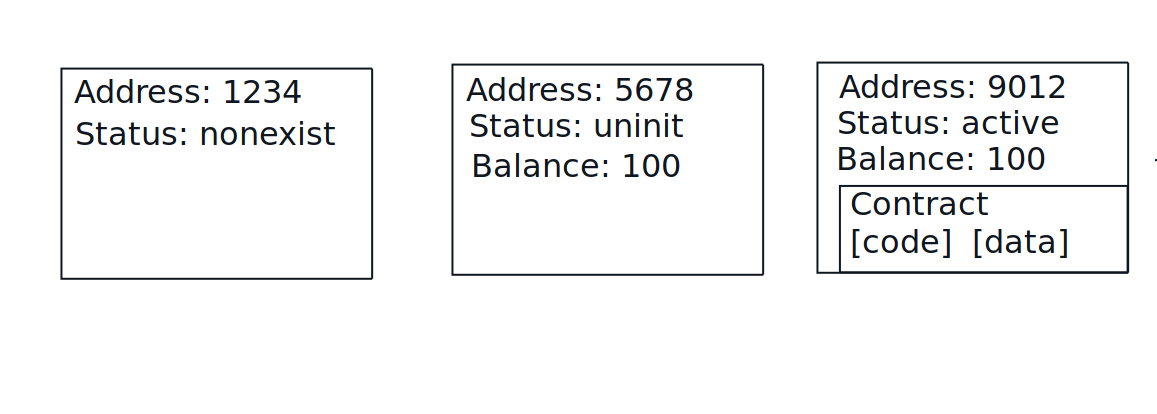

Account addresses
The internal address of an account is a pair of two numbers: its workchain ID and a 256-bit number. It may be displayed in the raw format (e.g.,0:4098805d2272a61b375350c6b2f5faaaf27c8267d8e7521ff2045104fdc7de76), but is usually shown in a user-friendly format (e.g., UQBKgXCNLPexWhs2L79kiARR1phGH1LwXxRbNsCFF9doczSI).
Messages
Addresses specify where messages should be delivered. There are three types of messages:- internal messages are sent between accounts;
- incoming external messages are sent from code outside the blockchain to a contract;
- outgoing external messages are broadcast to the external network; somewhat similar to adding them into the globally available list of all outgoing external messages that ever happened.
active.
StateInit
A message might also be a deploy message if it has a StateInit structure attached with its initial code and data. When such a message is sent, the hash of StateInit must match the destination address. If it does, the code and data are stored in the account at that address, and the account becomes active. Both the code and data stored in the account may change in the future, but its address will remain the same as when it was originally deployed.
Transactions
Formally, a message is only an intent: it has a destination, possibly some Toncoin, and data. After the message is handled and all the necessary changes are applied to the blockchain, the message is packed, along with a description of those changes, into a single packet of data, called a transaction. A transaction records the state changes on an account. Some transactions might happen without any message.TON Virtual Machine
Internal and incoming external messages execute the account’s code. The code is interpreted by TON Virtual Machine (TVM). It is written in bitcode, a binary format specific to TVM. In the future, TVM might support multiple binary languages, codepages, but at the moment there is only codepage 0 (CP0).
Phases
When execution starts, the message and current account state are provided to the code. By the end of execution, the account might change its state or code, or send internal or outgoing external messages. The execution follows a process whose steps are called phases. Fees are deducted during this process. Fees might be deducted from the account’s balance or from the Toncoin the message carries, depending on the mode of the message, or by explicit choice made in the contract’s code.Gas
Execution cost is first measured in gas units, then converted to Toncoin. This unit is separate so that if code execution becomes computationally cheaper (or more expensive), validators can vote to change the price of gas in Toncoin.Exit codes
If something goes wrong, a non-zero exit code might be returned, no changes to state or code are saved, and no further messages are sent. If the message that resulted in a failed transaction is marked as bounceable, a bounce message is sent back to the sender. Bounce messages are used to inform the sender that handling of their message failed. They can carry either truncated or full body of the original message.Traces
The most common reason a code is executed is when some account has received a message. Internal messages can only be sent by another contract executing some code, and that contract must have received a message from somewhere too. In the end, every message can be considered part of some trace: a tree of messages between accounts that starts with an incoming external message, continues with internal messages, and possibly ends with some outgoing external messages.Asynchronous execution
When some interaction with the blockchain involves multiple contracts, their code is not executed in the same block. Contracts have to exchange messages with each other, and two such concurrent traces may interleave their messages. This fact is usually referred to as “asynchronous message handling.” This feature of TON allows a limit to be placed on the maximum complexity of atomic computation and aids its scalability, but it is important to keep it in mind because it might create race conditions.Languages
Most development is done in the Tolk, a high-level programming language. Its compiler is included in the Blueprint development environment and will be available to all projects created from the template. Originally, Fift, a Forth-like assembly language, and FunC, a C-like intermediate-level language, were used for contract development.Get methods
If an external service needs to extract data from the blockchain, it can call a get method: an arbitrary function implemented in the code deployed to an account. Every call of a get method spawns a separate instance of TVM. Any changes to the blockchain made during the execution of a get method are not committed to the blockchain. Unlike in other blockchains, get methods cannot be called by other contracts. It is intentional for several reasons:- by the time another contract receives the result of such a call, other messages may have been processed and may have changed the result;
- get methods are executed completely separately, and changes from the blockchain are not guaranteed to be propagated to the server running the code of a get method.
Wallets
The main user of incoming external messages is a wallet. A wallet is an account with a specific kind of smart contract deployed on it, which can handle incoming external messages, specifically transfer messages. A transfer message is a request to send an internal message to another account. Thus, a wallet transforms incoming external messages to internal messages.Wallet contract types
There are several implementations of wallets, with varying extra functionality and protection.V5R1 is the latest official general-purpose wallet. The text below describes only the functionality common to most wallets.
How wallets work
A transfer message consists of a destination address and, optionally, an internal message, both serialized and signed with a private key. The wallet stores a public key and uses it to check that a transfer message was signed with the corresponding private key. If the check succeeds, it sends that internal message to the destination address. This ensures only the user (or a service) who knows the private key can use the wallet. Private and public keys are generated in a program or service outside the blockchain. Public key is used in aStateInit during the deploy, and determines the address of the wallet account. Keypair is usually derived from a set of 24 random words called a mnemonic.
Before the code of the wallet can be deployed on an account with an incoming external message, some other account has to transfer Toncoin to the wallet account. As external messages cannot have any Toncoin attached to them, if no funds are in the account when it handles an external message, it cannot pay for the message that deploys a wallet. The transfer of Toncoin to a wallet account usually comes from an exchange or another user. In testnet, there is a bot that sends test coins to an account for free.
Usually, a transfer message is sent without an internal message in its payload and only instructs the wallet to transfer some Toncoin to a destination address. This is the reason this type of smart contract is called a wallet.
An internal message might be a request to some other contract or even a deploy message that deploys code on other accounts. In this way, a wallet acts as a proxy between a user (or an external service) and the rest of the blockchain.
Wallet apps
End users usually use wallet apps to create and use wallets. An exchange will usually create a wallet for a user as well.Standard contracts
The other important types of contracts are- Jetton tokens roughly correspond to coins and allow developers to mint their own currency;
- NFT tokens are similar to tickets: unique items that can be sold;
- SBT tokens are like medals: unique items that can be given to someone but can never be sold or transferred.
Explorers
An explorer is a type of web app that displays information about the current state of accounts (including wallets, Jettons, and NFTs) and the history of transactions.APIs and SDKs
To interact with wallets, Jettons, and other contracts, data has to be sent through an ADNL or HTTP API into the network. There are several ways to connect:- directly call the API, or
- use an SDK that simplifies working with an API by wrapping its methods in a more user-friendly interface; the most popular TypeScript SDK for this is
@ton/ton.
TON Connect
When an application has to use a wallet to prove the user’s identity, it needs access to the wallet’s private key. Giving arbitrary applications access to the private key is insecure, as they could perform arbitrary actions with the wallet. To address this, there is the TON Connect set of SDKs that provide interfaces- for an application to perform an action through the wallet app;
- for a wallet app to handle these requests.
Data storage model
All data on TON is stored as trees of cells: the state of contracts, their code, and messages. Each cell stores up to 1023 bits of data and can have up to 4 refs to other cells. Each cell has a hash computed from its bits and refs. Because the hash of a cell that directly or indirectly references itself would require knowing the same hash, creating cyclic data structures is impossible. Standard serialization of such a data structure into a single binary string is the bag of cells (BoC). Compilers of smart-contract programming languages produce a BoC with code. When there is a need to store cells in a file or send them over the network, they are usually serialized into a BoC.Binary representation
To tell other developers how a certain type of data is stored in cells, a TL-B schema language is used. Its purpose is similar to that of protocol buffers or binary templates, but it provides more features for structuring data at the bit level. There are libraries for assembling data structures out of cells. For TypeScript, the most popular one is@ton/core.
The TL-B schemas for binary representations of messages, transactions, initial contract state, and most other data structures used by the blockchain can be found in the block.tlb file in the TON monorepo. TypeScript functions for serializing and deserializing them are provided by the @ton/core and @ton/ton libraries.
In general, a library that converts data structures between cells and the format native to a programming language, or allows calling contract methods as native functions of the language, is called a wrapper or binding. For example, functions that deserialize Jetton-related cell data into TypeScript objects can be found in the assets-sdk library. Some high-level programming languages can generate bindings from the contract’s source code. The “rule of thumb” is that production-grade code should not include low-level manipulation of binary data, and should instead rely on a library with bindings. This reduces the chance of mistakes and ensures the code has more users. With widely reused code, there are more opportunities to detect mistakes, and they are more likely to be fixed quickly.